Services
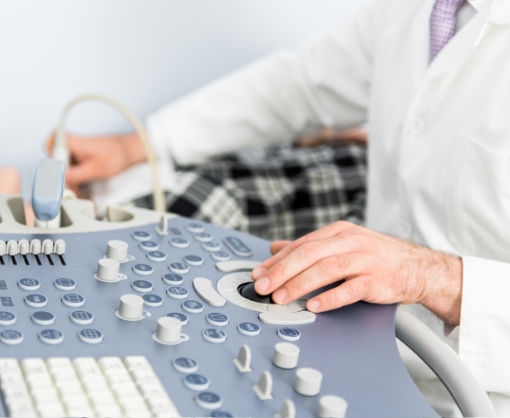

Doppler / ultrasonography:
Ultrasound is used to visualize the vessels supplying the brain in order to assess constrictions or occlusions, risks of a stroke. The examination is painless.
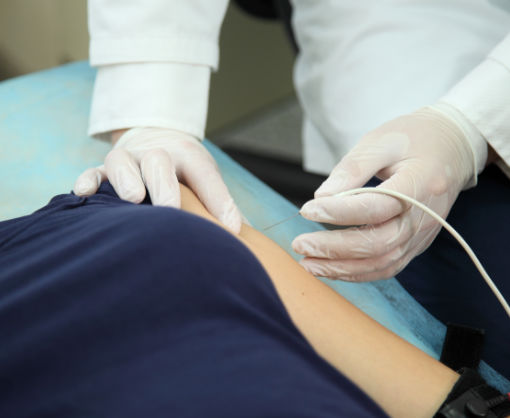
Electroneurography:
The conductivity and thus the function of the peripheral nerves can be measured by current pulses. This examination is used in particular for diseases such as carpal tunnel syndrome or polyneuropathies. The examination is harmless, but can be felt as unpleasant due to the current impulses.
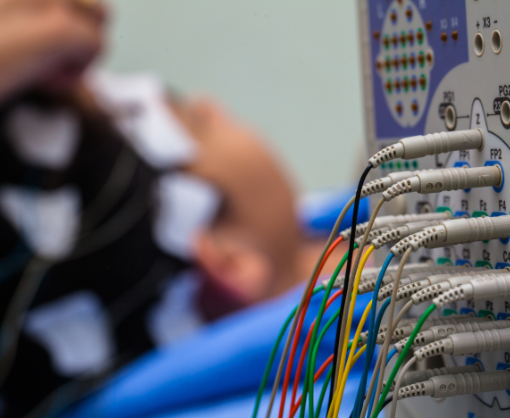

Electroencephalography (EEG):
In this examination, electrodes are placed on the scalp, which derive the electrical activity of the brain and make it visible on a screen. This is used to diagnose or monitor seizure disorders such as epilepsy. The examination is painless.
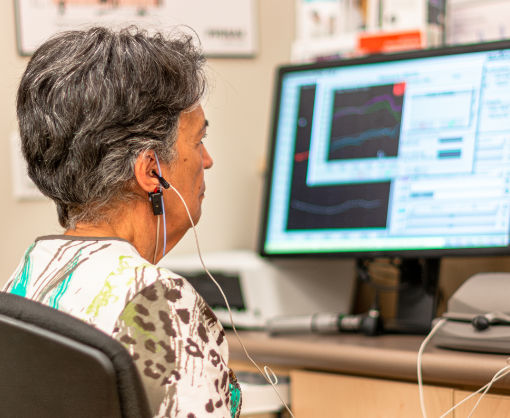

Evoked potentials:
This includes a series of examinations in which the functioning of various nerve pathways is measured by stimulating sensory organs or peripheral nerves. The impulse triggered by the stimulation can be recorded and assessed.
Among other things, the following are examined: the visual pathway (visually evoked potentials, VEP), the auditory pathway (acoustically evoked potentials, AEP) or the sensory system (somatosensory evoked potentials, SSEP). These tests are used for a variety of diseases, e.g. in multiple sclerosis, spinal cord diseases or polyneuropathies.
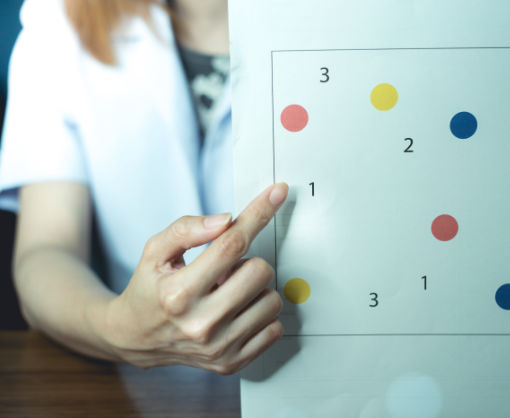

Psychometric testing and medical reports:
Various test procedures are carried out, which can reveal cognitive disorders such as memory impairment, attention deficit or disorientation. These procedures help to narrow down underlying diseases (e.g. Dementia).
Finally, medical reports for court cases, insurance institutions and several associations as well as traffic medical reports for neurological diseases are offered at our surgery.
